Comparative Gene-Expression Analysis I: Hybridization-based techniques
-
00:00
1.
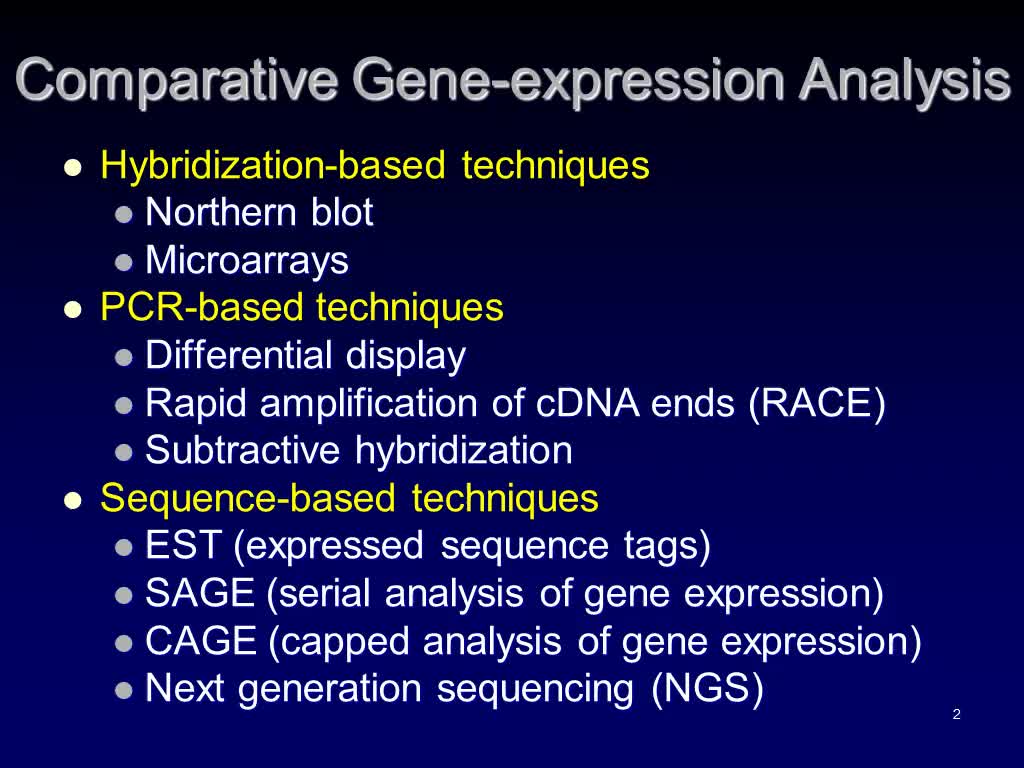
Comparative Gene-expression Analysis
-
00:15
2.
Question
-
00:40
3.
Differential Display
-
01:20
4.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
-
04:15
5.
Template DNA
-
07:24
6.
SpecificityMust be complementary to flanking sequences of target regionNot be complementary to other non-target regions of genomeNested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR): to reduce non-specific binding Primer LengthToo short lack specificityToo lon
-
08:56
7.
Product SizeBasic Taq polymerase can easily amplify fragments up to 1,000 to 2,000 bpTypical qPCR amplicons are 70-200 bp in lengthToo long Fluorescent intensity not in linear rangePrimer DimersIf the primers have self-complementary sequences, the prime
-
11:35
8.
General Considerations in Primer Design
-
16:45
9.
General Considerations in Primer Design
-
18:02
10.
G/C ContentPrimers should be about 50% G/C (40~60%) Not have long runs of G/C or A/T (>3 bp) A stretch of A/T’s might only weakly base pairA stretch of G/C might promote mis-annealingG/C clampTo ensure the stability of this interaction, primers are often
-
18:45
11.
Web Based Tools for Primer Design
-
18:52
12.
http://biotools.nubic.northwestern.edu/OligoCalc.html
-
19:02
13.
Web Based Tools for Primer Design
-
19:08
14.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/
-
19:13
15.
Question
-
20:23
16.
Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
-
21:50
17.
Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
-
22:51
18.
Multiplex PCR
-
25:04
19.
Primer Design Assistant
-
25:13
20.
PCR-based Techniques: Subtractive hybridization
-
28:41
21.
QuestionCan RNA be amplified directly by PCR? Why and why not?
-
29:39
22.
Reverse Transcription PCR
-
31:40
23.
Real Time - PCR
-
34:45
24.
Real Time - PCR
-
37:27
25.
Amplification Plot
- 索引
- 筆記
- 討論
- 全螢幕
Comparative Gene-Expression Analysis II: PCR-based techniques (0323)
長度: 41:55, 瀏覽: 819, 最近修訂: 2021-03-30
-
00:00
1.
Comparative Gene-expression Analysis
-
00:15
2.
Question
-
00:40
3.
Differential Display
-
01:20
4.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
-
04:15
5.
Template DNA
-
07:24
6.
SpecificityMust be complementary to flanking sequences of target regionNot be complementary to other non-target regions of genomeNested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR): to reduce non-specific binding Primer LengthToo short lack specificityToo lon
-
08:56
7.
Product SizeBasic Taq polymerase can easily amplify fragments up to 1,000 to 2,000 bpTypical qPCR amplicons are 70-200 bp in lengthToo long Fluorescent intensity not in linear rangePrimer DimersIf the primers have self-complementary sequences, the prime
-
11:35
8.
General Considerations in Primer Design
-
16:45
9.
General Considerations in Primer Design
-
18:02
10.
G/C ContentPrimers should be about 50% G/C (40~60%) Not have long runs of G/C or A/T (>3 bp) A stretch of A/T’s might only weakly base pairA stretch of G/C might promote mis-annealingG/C clampTo ensure the stability of this interaction, primers are often
-
18:45
11.
Web Based Tools for Primer Design
-
18:52
12.
http://biotools.nubic.northwestern.edu/OligoCalc.html
-
19:02
13.
Web Based Tools for Primer Design
-
19:08
14.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/
-
19:13
15.
Question
-
20:23
16.
Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
-
21:50
17.
Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
-
22:51
18.
Multiplex PCR
-
25:04
19.
Primer Design Assistant
-
25:13
20.
PCR-based Techniques: Subtractive hybridization
-
28:41
21.
QuestionCan RNA be amplified directly by PCR? Why and why not?
-
29:39
22.
Reverse Transcription PCR
-
31:40
23.
Real Time - PCR
-
34:45
24.
Real Time - PCR
-
37:27
25.
Amplification Plot
- 位置
-
- 資料夾名稱
- 2021
- 發表人
- 賴亮全
- 單位
- 賴亮全教授
- 建立
- 2021-03-23 22:40:17
- 最近修訂
- 2021-03-30 20:16:27
- 長度
- 41:55